The process of 3D animation production typically involves several key steps. While the specific workflow can vary depending on the project and studio, here are the general steps involved in producing a 3D animation fantasy product:

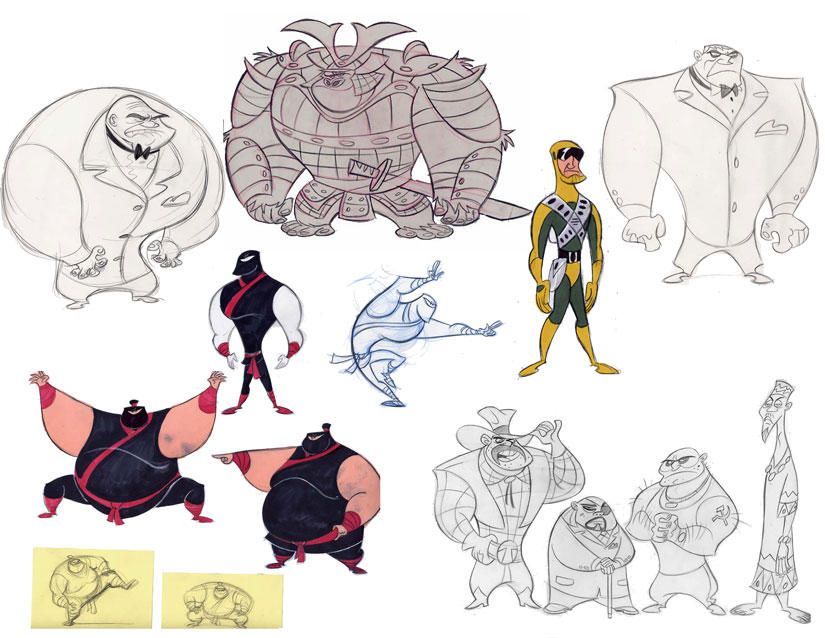
- Concept Development: This is the initial stage where ideas are brainstormed, and concepts for the animation and fantasy are developed. Storyboards and concept art may be created to visualize the animation. The main Specifications of a Well-Developed Animation Concept are:
- Unique and Engaging Story: A well-developed animation concept should have a captivating and original storyline that hooks the audience’s attention. It should offer something fresh, fantasy and unique, distinguishing it from existing content.
- Strong Characters: The concept should feature well-defined and relatable characters with distinct personalities, motivations, and arcs. Each character should contribute to the overall narrative and have room for growth and development.
- Visual Appeal: A visually appealing concept is crucial for animation. Whether it’s the overall art style, character designs, or vibrant backgrounds, the visual elements should be aesthetically pleasing and cohesive, complementing the story being told.
- Emotional Resonance: An effective animation concept evokes emotions and fantasy in the audience. It should have moments of joy, sadness, excitement, or inspiration, allowing viewers to connect with the characters and their journey on an emotional level.
- Strong Themes and Messages: A well-developed animation concept often explores meaningful themes and conveys important messages. It should offer valuable life lessons, promoting positive values, diversity, inclusivity, or environmental awareness.
- Marketability: Consideration of the target audience and potential marketability is crucial. The concept should have the potential to appeal to a wide range of viewers while maintaining a unique identity that sets it apart from competitors.
- Concept Development: This initial stage of animation production is where ideas are brainstormed and refined. It involves the creation of storyboards and concept art to visualize the animation’s key elements and provide a foundation for further development. Brainstorming sessions allow for the exploration of various ideas, characters, settings, and storylines. From these sessions, a concept starts to take shape, with a clear focus on the story’s central theme, tone, and overall direction. Storyboards and concept art serve as visual aids, helping to convey the intended look and feel of the animation. They provide a glimpse into the world and characters, assisting in determining the visual style, pacing, and composition. The concept development stage is crucial for establishing a strong foundation for the animation’s creative direction and serves as a reference point for subsequent production steps. It allows the animation team to ensure that the core elements of the concept align with the desired goals, ensuring a cohesive and engaging final product.
- Pre-production: In this phase, the script is refined, characters are designed, and a detailed plan is created. This includes creating a shot list, developing the animation style, and creating a production schedule.
- Pre-production is a crucial phase in animation production. During this great and important stage, the script undergoes refinement, ensuring a solid foundation for the story. Character design takes place, with artists creating visual representations of the characters, capturing their appearance, personality, and traits. A shot list is created, mapping out the key shots and sequences of the animation. The animation style is also developed, determining the visual look and feel of the project. Additionally, a production schedule is established, outlining the timelines, milestones, and resource allocation for the project. Pre-production sets the groundwork for the subsequent stages, ensuring a clear plan and direction for the animation production process.
- Modeling: The 3D models of characters, props, and environments are created using specialized software. The models are built with polygons or other geometric shapes, and textures and materials are applied to them.
- Modeling is a identical step in 3D animation production. Specialized software is used to create detailed 3D models of characters, props, and environments. The models are built using polygons or other geometric shapes, carefully sculpted and refined to achieve the desired appearance and structure. Once the models are created, textures and materials are applied to give them a realistic or stylized look. Texturing involves adding surface details, colors, and patterns, while materials determine how the models interact with light and simulate various physical properties. Modeling lays the foundation for the visual elements of the animation, bringing the virtual world to life with intricately designed and textured 3D assets.
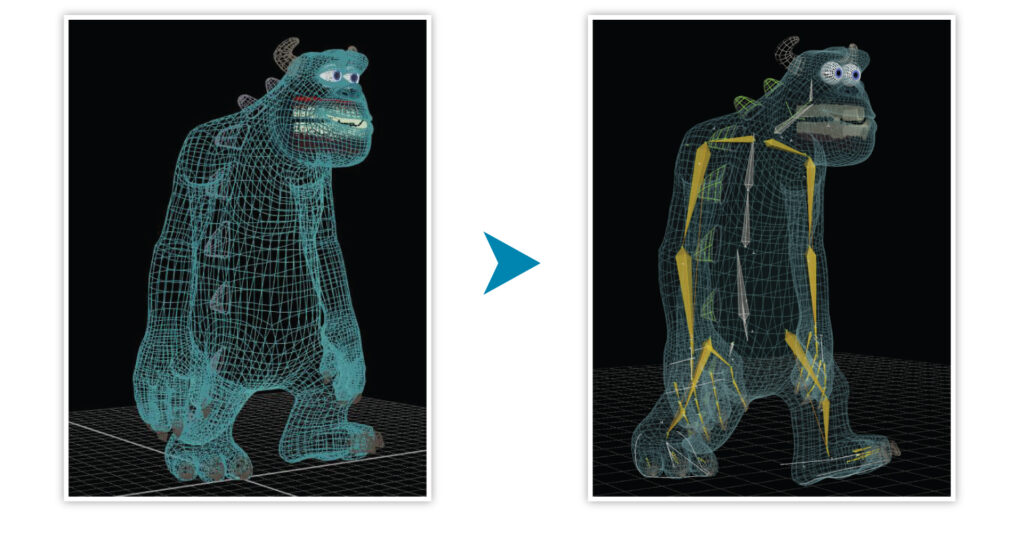
- Rigging: Rigging involves creating a digital skeleton (rig) for each character or object in the 3d animation. The rig allows animators to manipulate the models and control their movements and deformations.
- Rigging involves creating a digital skeleton, known as a rig, for each character or object. The rig serves as a framework that enables animators to manipulate the 3D models and control their movements, expressions, and deformations. Through rigging, animators can define joints, controls, and constraints, allowing for realistic movements and expressions. This process includes setting up the rig hierarchy, creating IK (inverse kinematics) systems, and implementing controls for easy manipulation. Rigging is essential in giving life to the characters and objects in the animation, enabling them to move and perform in a believable and expressive manner.
- Texturing and Shading: This step involves adding surface details, textures, and colors to the 3D models. Texturing gives the models a realistic or stylized appearance, while shading determines how the materials interact with light.
- Texturing involves adding surface details, textures, and colors to the 3D models, enhancing their realism or stylized appearance. Textures can simulate materials like skin, metal, fabric, or wood, adding depth and richness to the models. Shading, on the other hand, determines how the materials interact with lighting in the virtual environment. It involves defining the properties of materials such as reflectivity, transparency, and glossiness. By carefully crafting textures and shading, animators bring life and visual appeal to the 3D models, making them more believable and engaging to the audience.
- Animation: Animators bring the 3D models to life by creating keyframe poses or using motion capture data. They refine the movements and performances of characters, objects, and cameras to convey the desired actions and emotions.
- Animation is the most influential and fundamental step in 3D animation production. Animators breathe life into 3D models by creating keyframe poses or utilizing motion capture data. They meticulously refine the movements, expressions, and performances of characters, objects, and cameras to convey the desired actions, emotions, and storytelling elements. Through skillful manipulation of the models, animators bring characters to life, imbuing them with personality, fluidity, and believability. They carefully consider timing, weight, and dynamics to create realistic or stylized animations that captivate audiences and effectively communicate the narrative of the animation. Animation is a vital element that adds depth, engagement, and emotional impact to the final product.
- Lighting: Lighting artists set up virtual lights and adjust their properties to create the desired mood, atmosphere, and realism within the scene. They also consider the interaction between light and materials.
- Lighting is the step that gives a fantasy and mythological beautification to the animation production. Lighting artists play a pivotal role in setting up virtual lights and adjusting their properties to create the desired mood, atmosphere, and realism within each scene. They consider factors such as the scene’s narrative, time of day, and location to effectively illuminate the 3D environment. Additionally, lighting artists take into account the interaction between light and materials, ensuring that surfaces accurately reflect and react to light sources. By skillfully manipulating lighting elements, they enhance the visual appeal, depth, and emotional impact of the animation, bringing the virtual world to life with convincing and immersive illumination.
- Rendering: Rendering involves processing the 3D animation scene to generate the final images or frames of the animation. This step can be time-consuming, as it requires significant computational power to calculate the lighting, shadows, reflections, and other visual effects.
- Rendering is the stage in 3D animation product that give it a fine crafted and fantasy looking. It involves processing the 3D animation scene to generate the final images or frames of the animation. This computationally intensive process calculates the interactions of light, shadows, reflections, and other visual effects within the scene. Rendering transforms the 3D models, textures, lighting, and other elements into a cohesive and visually appealing final result. It can be a time-consuming process, especially for complex and highly detailed scenes, as it requires substantial computational power. The quality of the rendering greatly influences the overall visual fidelity of the animation, ensuring that the final images or frames meet the desired standards of realism, artistic vision, and technical precision.
- Visual Effects (VFX): Additional visual effects can be added during the post-production stage to enhance the 3D animation. This may include particle effects, simulations, compositing, and color grading.
- Visual Effects (VFX) play a making up and improving role in enhancing 3D animation during the post-production stage. VFX artists add supplementary visual elements to elevate the overall visual appeal and impact of the animation. This can include particle effects like fire, smoke, or explosions, as well as simulations such as cloth or fluid dynamics. Compositing techniques are used to merge various elements seamlessly, creating a cohesive and polished final result. Additionally, color grading is employed to enhance the mood, tone, and overall aesthetic of the animation. VFX artists employ their creativity and technical skills to bring additional visual enhancements fantasy to the 3D animation, making it more immersive, dynamic, and visually striking.
- Editing: The rendered frames are compiled and edited together to create the final sequence of the animation. This includes cutting, timing adjustments, adding sound effects, music, and voiceovers.
- Editing involves compiling and arranging the rendered frames to create the final sequence of the animation. Editors carefully select and cut the frames, ensuring a seamless flow and timing that aligns with the desired pacing and narrative. They make adjustments to the timing and duration of shots, enhancing the overall rhythm and impact of the animation. Additionally, editors add sound effects, music, and voiceovers, synchronizing them with the visuals to enhance the storytelling and emotional impact. Through the art of editing, the disparate elements of the animation come together, creating a cohesive and captivating final product that engages and delights the audience.
- Post-production: The final sequence is polished by applying color correction, adding final touches, and ensuring the audio and visual elements are synchronized. All of this serves to the fining of the product.
- Post-production is the final stage in the 3D animation production process. It involves polishing the final sequence by applying color correction, adding final touches, and ensuring the synchronization of audio and visual elements. Color correction adjusts the color grading to enhance the overall aesthetic and consistency of the animation. Final touches may include adding visual effects, fine-tuning animations, or refining details to achieve the desired level of quality. In addition, post-production ensures that the audio elements, such as sound effects, music, and voiceovers, are synchronized seamlessly with the visuals. This stage is crucial for fine-tuning the animation, ensuring that it meets the desired standards of excellence and delivers a polished, cohesive, and engaging final product to the audience.
- Distribution: Once the animation is complete, it can be distributed through various channels such as film festivals, online platforms, television, or other media outlets.
In arranging practical steps of a 3D animation production project, It’s important to note that this is a simplified overview, and the production process can vary depending on the complexity and requirements of the project. Each step involves a great team of artists and technicians working collaboratively to bring the animation to life.
If you want to turn your concept into an animated reality, then we are who you need. Visit our film showcases to understand better what we can do for you. Check Phoenix news to get regular updates on our ever-expanding services, such as facilitation.
Contact US today and begin the journey of turning your vision into a work of art. Also you are very welcome to Dubai – Business bay, to visit us at our Dubai branch office.
More blogs and news, kindly Follow the Phoenix Blogs …























